Key aspects of Supplement to Savings:
- It reveals only $59 billion in savings are currently being captured;
- It specifies the chronic diseases avoidable with preventive care;
- It reveals the nine supplements and intake levels needed to realize the additional billions in healthcare savings;
- It provides evidence that the use of certain dietary supplement ingredients by specific populations can reduce the direct and indirect medical costs associated with chronic diseases and conditions including coronary artery disease, osteoporosis, age-related macular degeneration, cognitive decline, irritable bowel syndrome, and childhood cognitive development disorders.
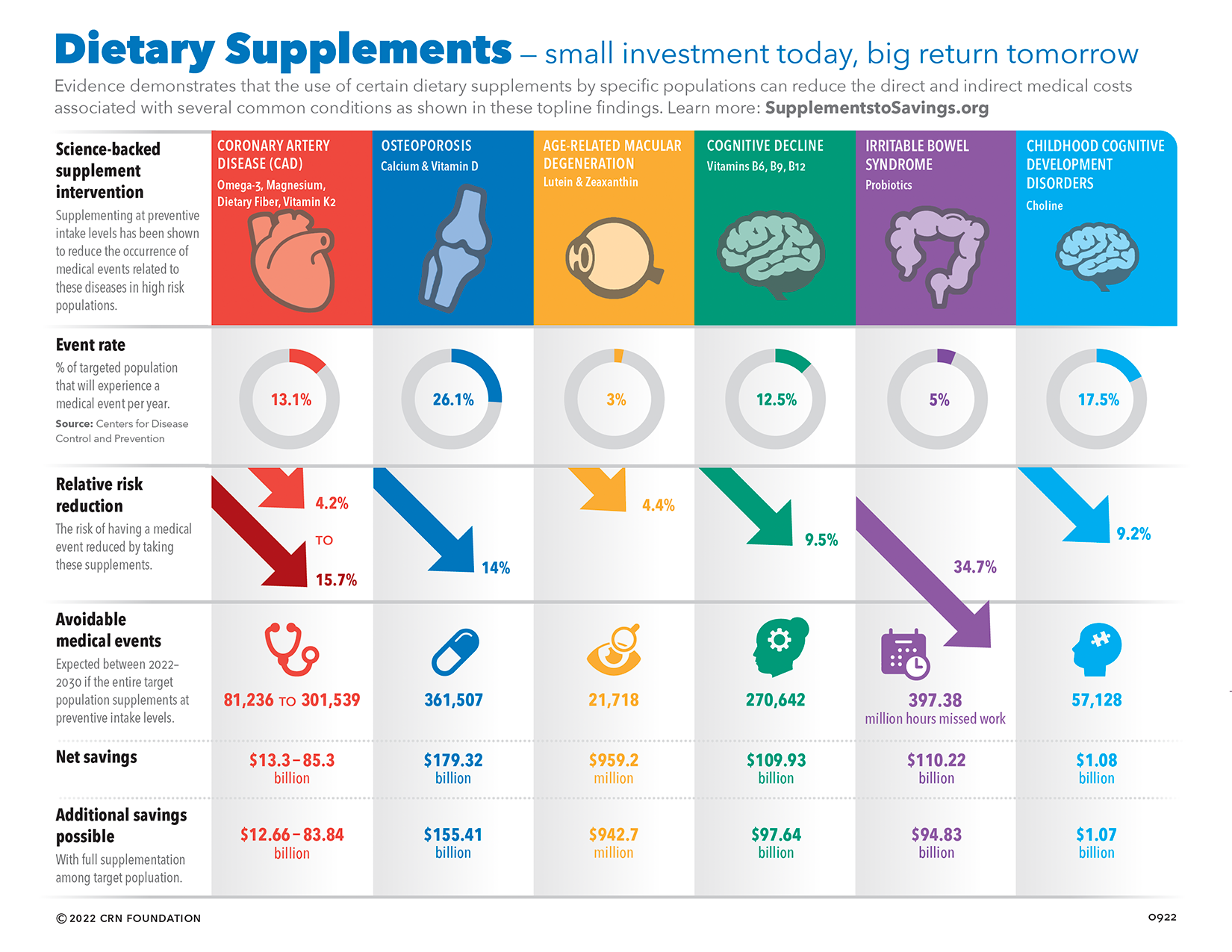
As CRN shared:
- The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that more than 75% of the nation’s healthcare spending is for people with chronic conditions.
- In addition to healthcare spending, these chronic diseases cost the U.S. more than $260 billion annually in lost workforce productivity.
- The U.S. invests less than 3% of total healthcare expenditures on preventive care services.










